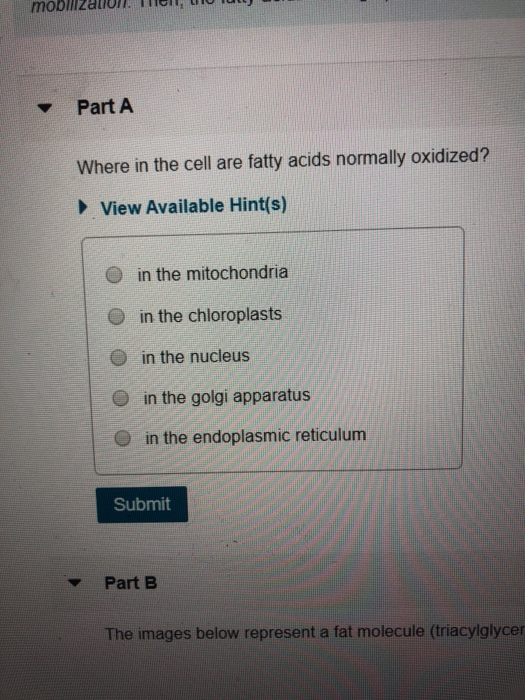
Where in the Cell Are Fatty Acids Normally Oxidized
The free FA concentration in blood is high which increases the FA uptake by the heart and allows the FAs to become the major source of energy and to account for up. What does Golgi apparatus do.
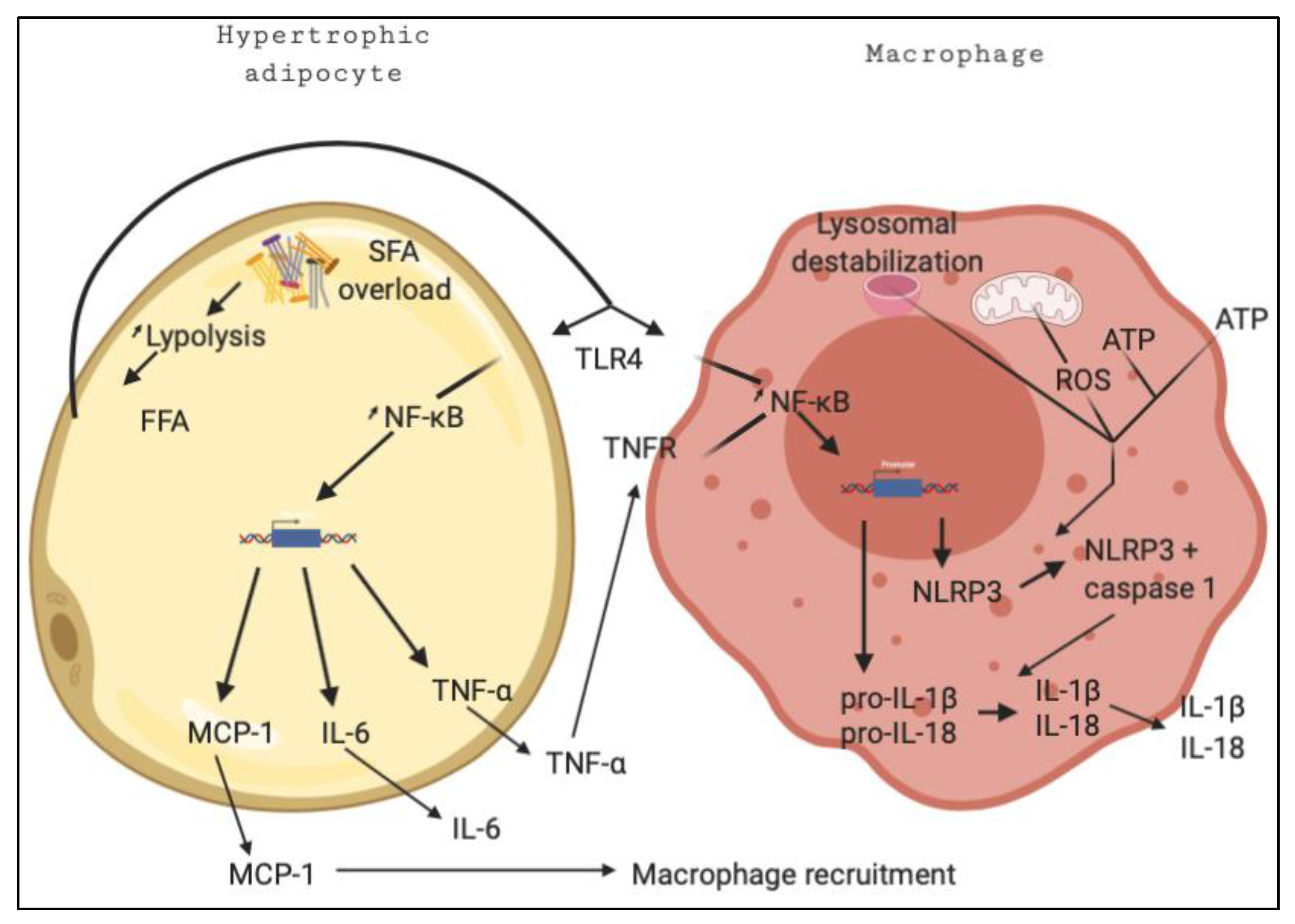
Ijms Free Full Text Monounsaturated Fatty Acids In Obesity Related Inflammation Html
One of the main byproducts of βoxidation is hydrogen peroxide which can be harmful to the cell.

. Then the original carboxyl group is removed as CO 2 leaving a shorter chain. A variety of substrates are broken down by such oxidative reactions in peroxisomes including uric acid amino acids and fatty acids. They are irregular in size and shape according to the cell and usually circular in cross-s e c ti on.
The acetyl groups are. The enzymes of fatty acid oxidation in animal cells are located in the mitochondrial matrix 172 Oxidation of Fatty Acids As noted earlier mitochondrial oxidation of fatty acids takes place in three stages. The cells of the central nervous system also do not use fatty acids for their energy requirements using instead carbohydrates or ketone bodies.
In the liver mitochondrial acetyl - CoA is used to synthesize ketone bodies acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate as alternative fuel sources for the brain and heart under conditions of carbohydrate scarcity 1316. This molecule is also carefully detoxified by the. AMACR catalyzes the chiral inversion of a variety of 2-methyl fatty acyl-CoAs and thereby regulates their entry into the peroxisomal or mitochondrial oxidation pathways.
Under normal conditions fatty acids are continuously supplied from the microvascular compartment to the contracting myocytes. Fatty acid oxidation is also referred to as β-oxidation because two carbon units are cleaved off at the β-carbon position second carbon from the acid end of an activated fatty acid. The first step in the digestion of this compound is the oxidation of the χ carbon by molecular oxygen.
The two pathways are distinct not only in where they occur but also in the reactions that occur and the substrates that are used. Fatty acid oxidation in the heart. Oxidation of fatty acids occurs in multiple regions of the cell within the human body.
Three general kinds of cancer named after the tissues. The process is normally a minor catabolic pathway for medium-chain fatty acids 10-12 carbon atoms but becomes more important when β oxidation is defective because of mutation or a carnitine deficiency for example. Fatty acid oxidation takes place in the mitochondrial matrix the inner compartment of mitochondria.
FIRST In the first stage β oxidation fatty acids undergo oxidative removal of successive two-carbon units in the form of acetyl-CoA starting from the carboxyl end of the. Transport of long-chain fatty acids across the muscular endothelium. At the end let us point out that the enzyme implied in the β-oxidation of fatty acids are mainly located in the mitochondria just like the enzymes responsible for electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation.
And omega-oxidation which occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum. Fatty acids are broken down to acetyl-CoA by means of beta oxidation inside the mitochondria whereas fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA outside the mitochondria in the cytosol. The oxidation of fatty acids Figure 1025 is a particularly important example since it provides a major source of metabolic energy.
The heart is known for its ability to produce energy from fatty acids FA because of its important beta-oxidation equipment but it can also derive energy from several other substrates including glucose pyruvate and lactate. AΑ-Methylacyl-CoA racemase AMACR functions in normal cells to enable oxidation of branched-chain fatty acids. View Available Hint s in the mitochondria in the chloroplasts O in the nucleus in the golgi apparatus in the endoplasmic reticulum Submit Part B The images below represent a fat molecule triacylglycel.
This chain can now be accommodated by the βoxidation reactions because. The mitochondria in which only Beta-oxidation occurs. During fasting the FAs are oxidized in the heart preferentially to other substrates.
As a result acetyl - CoA is generated in the mitochondria for oxidation or other possible fates. The ω omega-carbon the methyl carbon of fatty acids is oxidized to a carboxyl group in the endoplasmic reticulum. But mitochondria have two membranes that fatty acids have to cross before they reach the matrix.
When fatty acids are oxidized changes typically occur at the atomic level which are initiated by various enzymes. Researchers are working on treatments that will increase the oxidation of these fatty acids within the heart in order to prevent the lipotoxic effects. - fatty acid enters the cycle where it is oxidised by acyl-coA dehydrogenase hydrated and reoxidised - thiolysis occurs where the bond is cleaved by another acyl coA using the sulphur of the thiol - rounds of beta-oxidation occur until all the fatty acid has been oxidised to acetyl-CoA so can enter the citric acid cycle.
The compounds also need to be activated within a cells cytoplasm. Oxidation can then take place within cellular structures called mitochondria. Cancerous tumors can occur in almost any tissue of the body although some are more often affected than others.
This is another process in which the length of the carbon chain makes a difference. The results of this study suggest that fatty acids are obtained from nutrients rather than from fatty acid. Fatty acids are usually oxidized by most of the cells of tissues in the body except the RBCs.
Both skeletal and cardiac muscle cells rely heavily on the oxidation of long-chain fatty acids to utilize chemically stored energy for contractile work. Cancer is a disease in which cells somehow become activated into uncontrolled multiplication and thus produce an overgrowth or tumor composed of malformed malignanat cells. Fatty acids from adipocytes also can be used for ATP production in cancer cells.
Heart cell fully depends on energy derived from fatty acid oxidation. The effects of the lipotoxicity is treated with leptin therapy and insulin sensitizers. The peroxisome where alpha- and beta-oxidation occur.
Peroxisomal βoxidation allows fatty acids to access the citric acid cycle directly. Fatty acid oxidation β-oxidation in mitochondria produces acetyl-CoA for TCA cycle as well as the reducing equivalents NADH and FADH 2 for ATP production through OxPhos. TUURZULIONI O Part A Where in the cell are fatty acids normally oxidized.
β-oxidation that takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria and converts their fatty acid chains into two carbon units of acetyl groups while producing NADH and FADH 2. Lipotoxicity affects the pancreas when excess free fatty acids are found in beta cells causing their dysfunction and death.
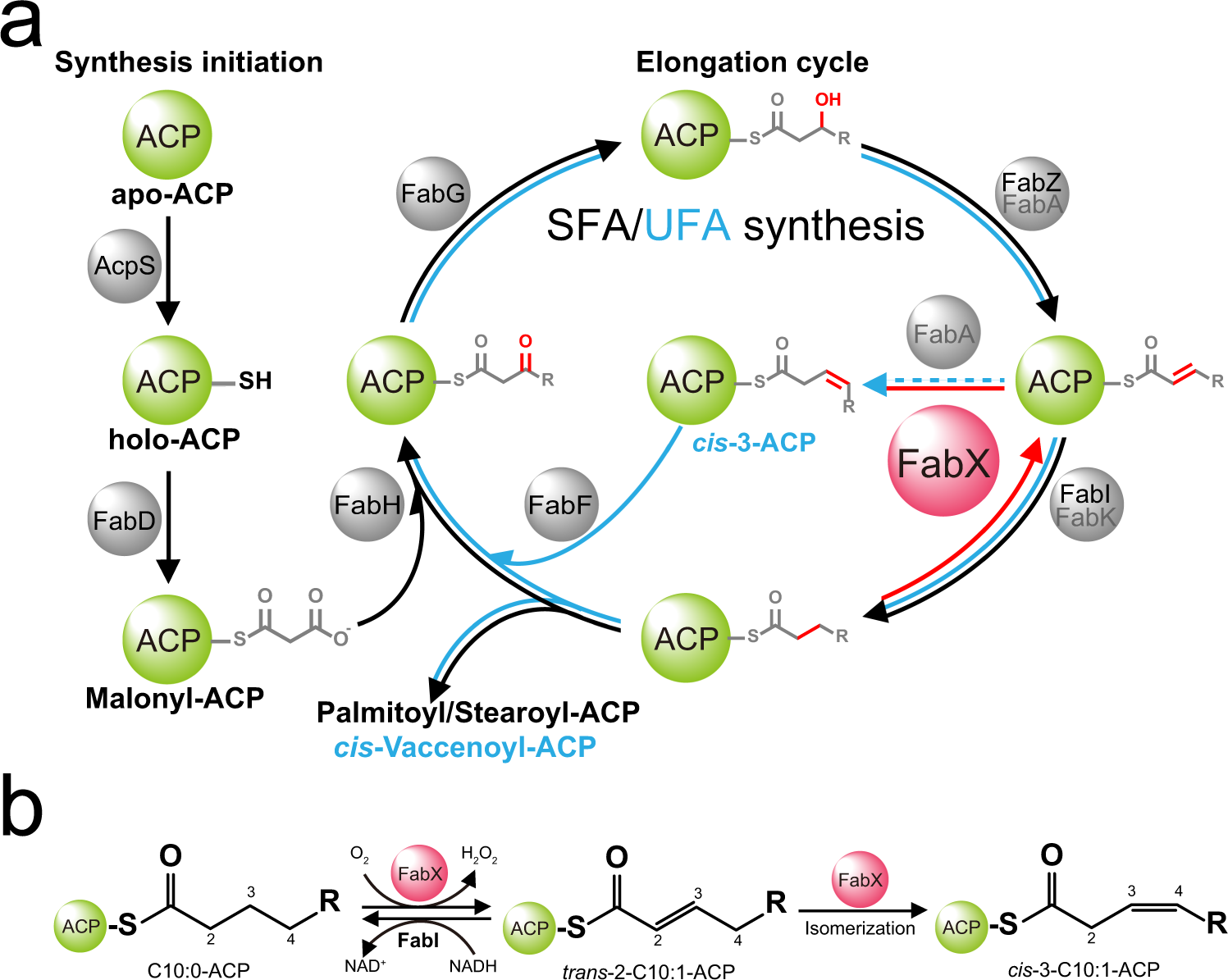
Helicobacter Pylori Fabx Contains A 4fe 4s Cluster Essential For Unsaturated Fatty Acid Synthesis Nature Communications

Lipid Saturated Fatty Acids Britannica

Oxidation Of Fatty Acids In Eukaryotes Sciencedirect
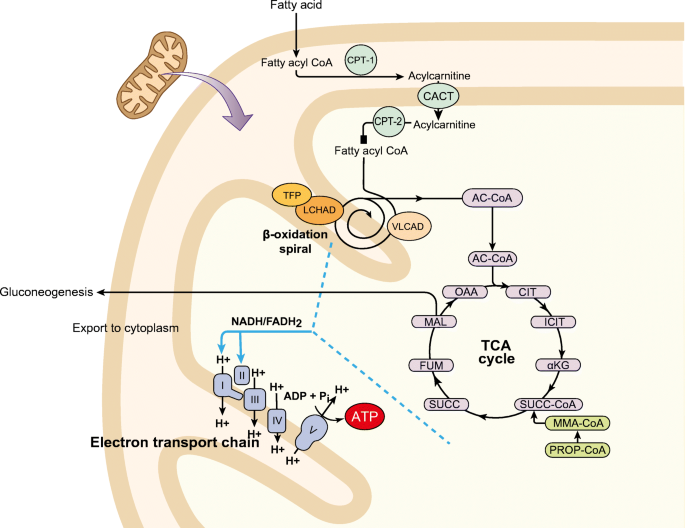
Clinical Manifestations And Management Of Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Springerlink
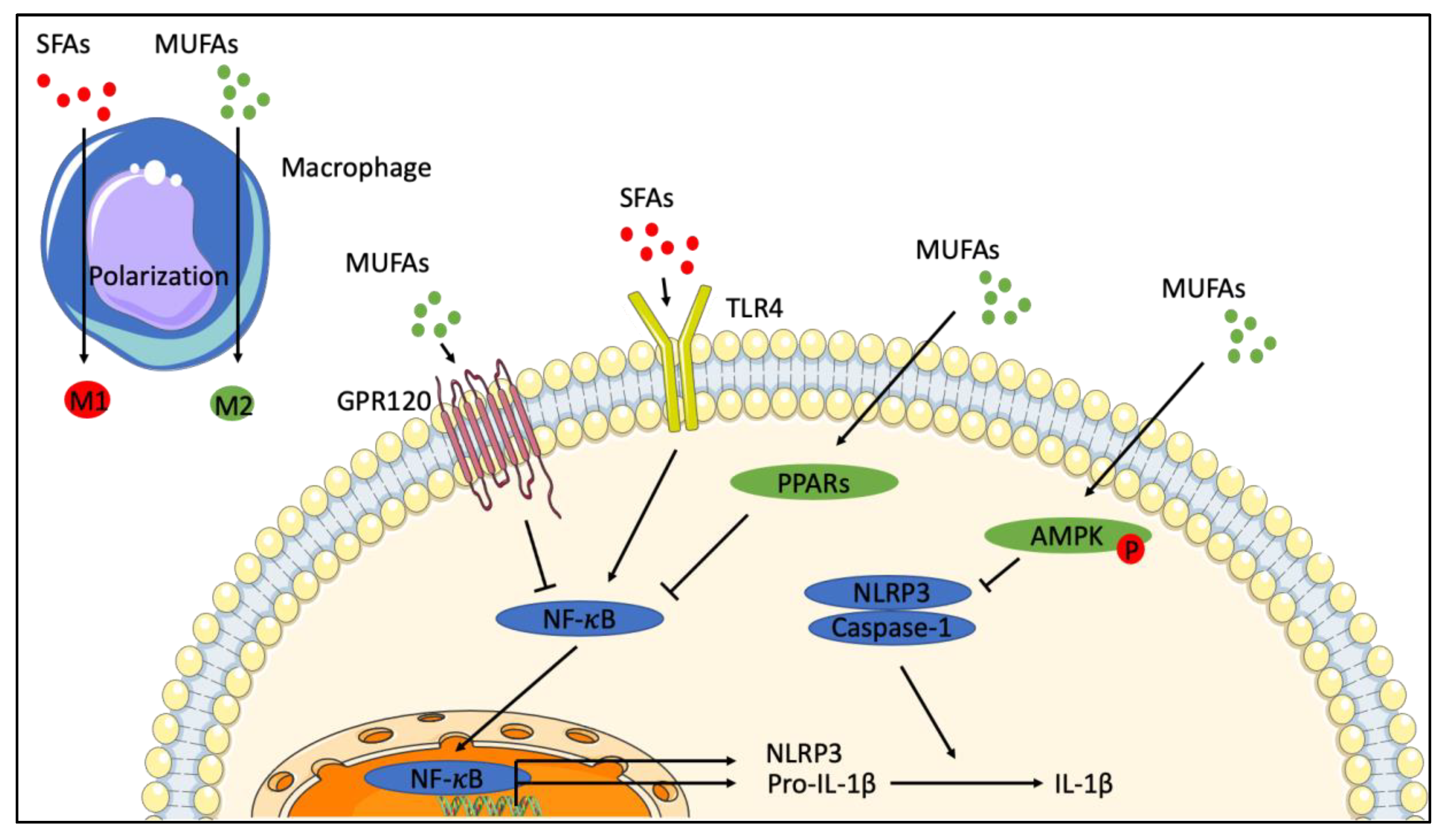
Ijms Free Full Text Monounsaturated Fatty Acids In Obesity Related Inflammation Html

Fatty Aldehyde An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
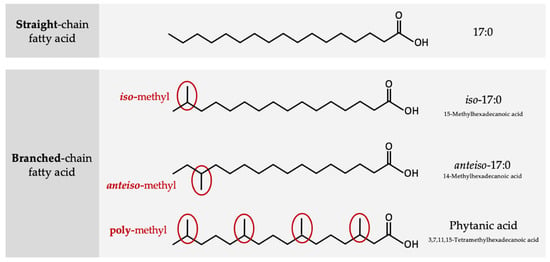
Nutrients Free Full Text Branched Chain Fatty Acids An Underexplored Class Of Dairy Derived Fatty Acids Html

Unsaturated Fatty Acid An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fatty Acid Transport An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Cd4 T Cell Differentiation And Function Unifying Glycolysis Fatty Acid Oxidation Polyamines Nad Mitochondria Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Lipid Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Lipid Mobilization Of Fatty Acids Britannica

Nitro Fatty Acid Logistics Formation Biodistribution Signaling And Pharmacology Trends In Endocrinology Metabolism

Saturated Fatty Acids An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Comparison Of Peroxisomal And Mitochondrial Fatty Acid B Oxidation Download Scientific Diagram
Solved Tuurzulioni O Part A Where In The Cell Are Fatty Chegg Com
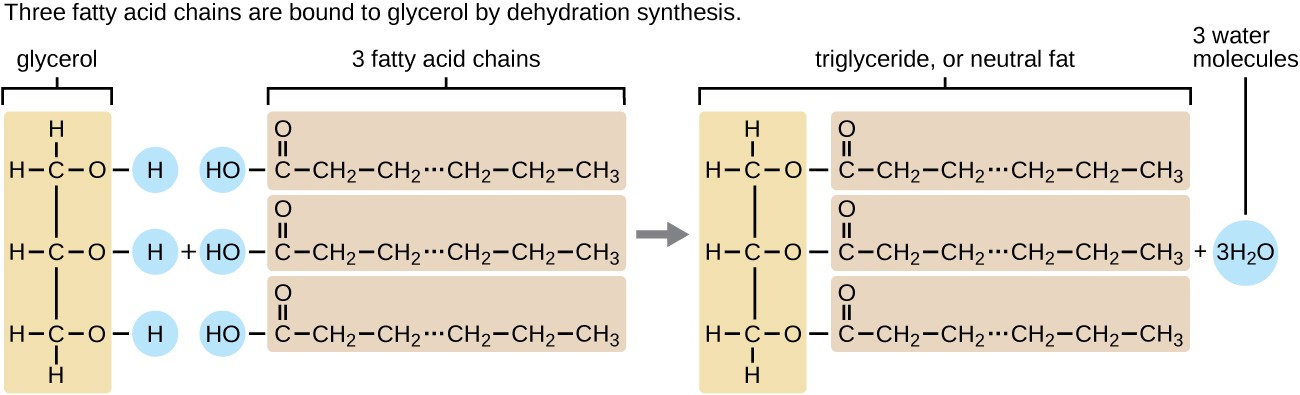


Comments
Post a Comment